he pharmaceutical industry has embraced digital transformation as a means of generating data that enables faster and better-informed decision making. Digitization has resulted in improved cohesion and overall effectiveness across the pharmaceutical value chain.
What are Digitized Medicines?
One such “smart” digitized oral medication solution involves the incorporation of spectrally encoded microparticles made of high-purity silicon dioxide, a material generally recognized as safe for ingestion by FDA (Figure 1). The microparticles are added onto tablets and capsules using existing processes and carriers.
Value of Digitized Medicines?
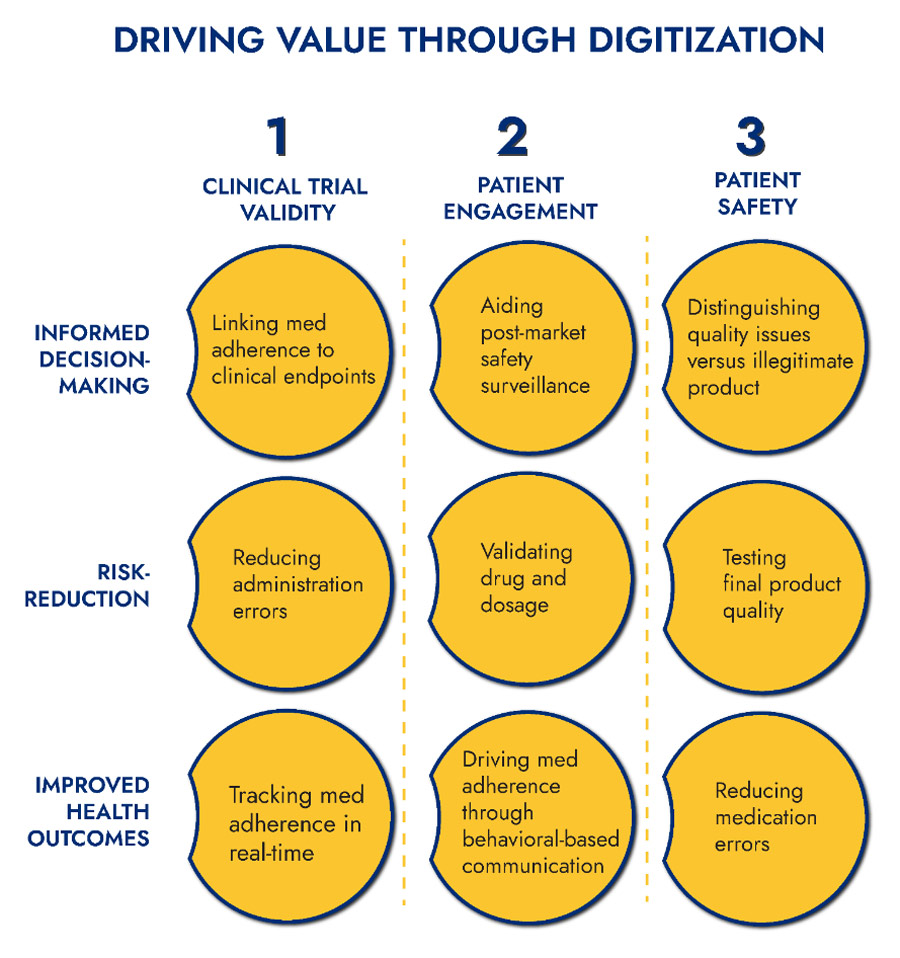
Improving Clinical Trial Validity through Digital Engagement
Linking patient engagement to clinical endpoints: Digitized medicine solutions offer patients the ability to directly interact with their medicines through smartphone applications. This engagement provides clinical trial administrators with a real-time view of participant medication adherence which can then be cross-referenced with clinical outcomes.
Identifying administration errors: Distribution of medicines in decentralized clinical trials is vulnerable to medication errors. Introducing digitized medicines into a trial has the potential to mitigate this risk by ensuring that the right patient has the right oral medication and dose. The ability for administrators to directly validate patients and medications is an enormous benefit in ensuring the integrity of decentralized trials. Critically, this can be achieved without affecting study blinding.
Improving Health Outcomes through Patient Digital Engagement Loops
Medication nonadherence is linked to poor health outcomes, increased hospitalizations, and even death. It costs healthcare systems billions of dollars on an annual basis. While reasons for medication nonadherence vary by patient, research suggests that most nonadherence is driven by communication and behavioral issues.
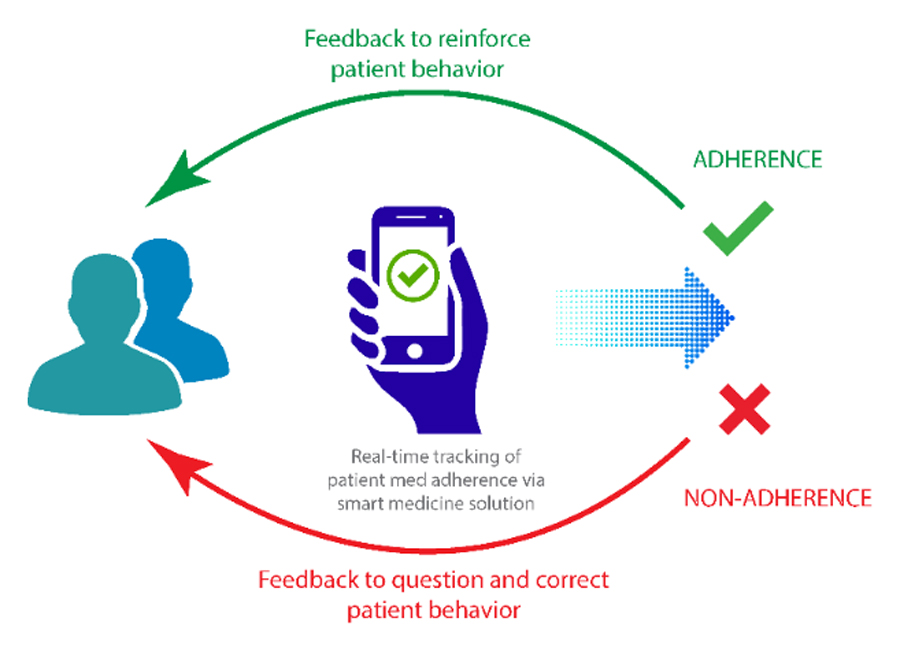
One approach to mitigating medication nonadherence is to use digitized medicine solutions to drive digital interventions that engage and educate patients while developing feedback loops that reinforce adherence and seek to change patient behavior (Figure 3).
Safeguarding the Patient through Digital Engagement
Mitigation of medication errors is another critical safety aspect that smart medicine solutions can address. In the US alone, it is estimated that medication errors cause at least one death every day and injure about 1.3 million people annually. By linking smart or digitized medicines to patient information, healthcare professionals can ensure that the right drug gets to the right patient in the right dosage.