South Korea MFDS: Improving Regulatory Science Based on R&D
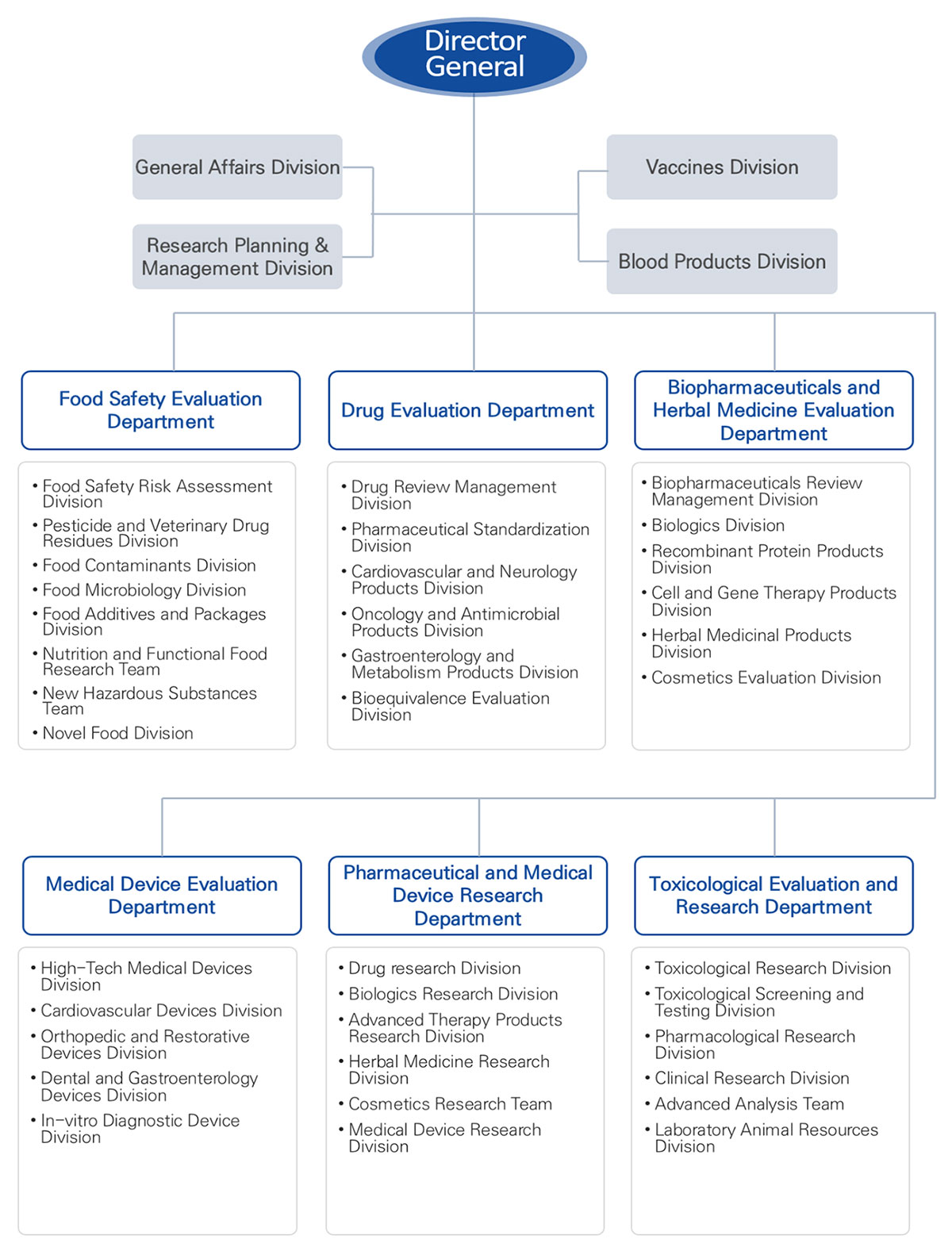
National Institute of Food and Drug Safety Evaluation (NIFDS)
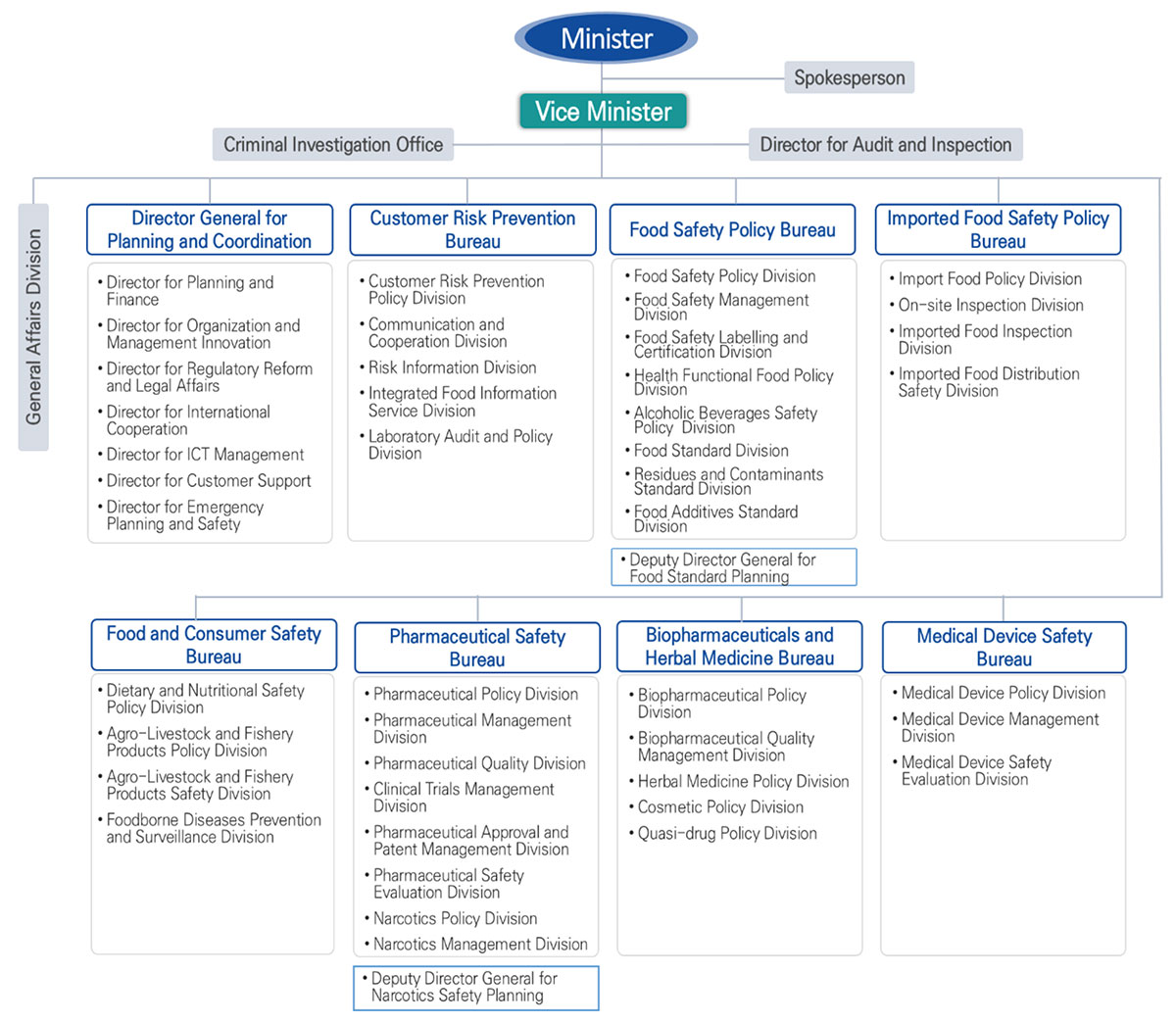
Ministry of Food and Drug Safety Evaluation (MFDS), South Korea
he Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) is a science-based regulatory agency responsible for the safety management of food, agricultural commodities, livestock and fishery products, drugs, biologics, herbal medicines, medical devices, quasi-drugs, cosmetics, and hygiene products to protect the public health. MFDS continues to expand its scope of product regulation by adopting new technologies to develop and establish strategies for regulatory science in Korea.
MFDS establishes new regulations in response to events in Korea, and sometimes accepts global regulations in the spirit of international harmonization. MFDS staff play an important role in joint expert groups, developing ICH guidelines, supporting the APEC Harmonization Center, discussing these topics and programs with DIA members (often including staff from other regulatory agencies), and other international harmonization activities.
Through its affiliate National Institution of Food and Drug Safety Evaluation (NIFDS), the MFDS also conducts research and development (R&D) to secure scientific evidence as the basis for safety management decisions and policies. Although the MFDS’ R&D budget is only 0.4 percent (about $80M US) of South Korea’s science and technology budget, it plays a crucial role in public health and patient relief. The NIFDS consists of six departments—three research departments and three review departments—which collaborate with each other on these R&D initiatives and provide scientific reviews for marketing approvals and risk assessment. While NIFDS staff conducts the actual R&D, they also collaborate with other researchers at universities and medical and other research institutions to take advantage of their high-quality scientific and human resources.
The law for the systematic and advanced regulatory science research on MFDS regulated products was established in 2015 and includes a five-year research development plan. The first five-year plan was implemented in 2016; the second five-year plan has already been prepared and includes MFDS’s future objectives and advanced strategies for regulatory science R&D. Five-year plans outline implementation plans for NIFDS’s research for every year.
MFDS-led R&D provides evidence for science-based standards and evaluation methods on safety, efficacy, and quality for MFDS-regulated products (medical drugs and devices) to safeguard public health. New tools, standards, or testing methods developed by MFDS R&D are utilized in regulations or guidelines for developing new drugs as well as the review and approval process for new drugs. MFDS staff also play key consulting and bridging roles in commercializing the accomplishments of R&Ds conducted by other government Ministries.
The MFDS sharpens safety technology knowledge and use through R&D in order to respond to the new emerging demands for safety management caused by aging population, climate change, and industry advances. Topics include innovative convergence products, RWD/RWE, safety measures based on epidemiological analysis, and advanced biologics such as cell therapies, related research, and changes in relevant systems. Innovative convergence products are combination drug products, biologics, and medical devices, which are not properly covered under the current Pharmaceutical Affairs Act and safety management system.
To address these challenges, the MFDS launched the new Innovative Convergence Products Support Department in March 2019. The Department manages product review and approval and drug classification while supporting research on review methodology and the management of convergence products. Research was initiated to study the necessity for and approaches to utilizing RWD/RWE for both post-approval management and in-approval processes.
The Act on the Safety Support for Advanced Regenerative Medicine (SSARM) and Advanced Biologics was enacted in August 2019. (Advanced regenerative medicine uses human cells and includes cell therapy, gene therapy, and treatment based on tissue engineering. Advanced biologics use living cells or are medicines containing genetic material and include cell therapy products, gene therapy products, and tissue engineering medicine.) The Act facilitates clinical trials on regenerative medicine that consider the unique characteristics of regenerative medicine and advanced biologics, providing new treatment options to patients who suffer from rare and incurable diseases. The SSARM Act allows for faster approval and helps with the establishment of a lifecycle safety management system that is suitable for the unique characteristics of advanced biologics, including sampling, production, and post-approval long-term tracking.
Rapid advances in science and technology will further increase the importance of MFDS’s role in regulatory science, giving greater responsibilities to MFDS in protecting the health and safety of Koreans through the proper safety management of MFDS-regulated products. To stay true to its mission, MFDS will keep preparing advanced strategies to overcome future challenges. By cooperating with research institutes nationally and abroad, the NIFDS will broaden its research capability and strengthen the MFDS’s ability to promote health within and beyond Korea’s borders.

