Future Pharmacovigilance: Industry Survey Reveals Trends and Strategies
n the intricate world of life sciences, where patient safety and regulatory compliance are paramount, pharmacovigilance (PV) stands as the guardian. To understand this dynamic landscape, a survey was recently conducted with a diverse pool of 100 PV professionals across the US and Europe. The findings unveiled a tapestry of compelling insights, spanning diverse themes encompassing PV team strategies, technology maturity, and the emergence of GenAI, etc. Notably, the survey (see details below) spotlighted intriguing statistics around the acceleration of automation, the embrace of AI/ML technologies, and the strategic evolution toward smart outsourcing, painting a vivid picture of the industry’s current trajectory.
- 100 PV professionals
- 95% Safety and PV operations, 5% IT operations for PV and safety
- 50% large, 25% midsize, 25% small pharmaceutical organizations
- 32% North America only, 28% global roles with North America as primary focus market, 14% EU5 countries only, 14% global roles with EU5 as primary target market
- 76% adverse event case management, 74% signal and risk management, 66% aggregate reporting
- 20% CXOs/EVPs/Presidents; 20% SVPs; 20% VPs; 40% Executive Directors, Senior Directors, and Directors
- 100 PV professionals
- 95% Safety and PV operations, 5% IT operations for PV and safety
- 50% large, 25% midsize, 25% small pharmaceutical organizations
- 32% North America only, 28% global roles with North America as primary focus market, 14% EU5 countries only, 14% global roles with EU5 as primary target market
- 76% adverse event case management, 74% signal and risk management, 66% aggregate reporting
- 20% CXOs/EVPs/Presidents; 20% SVPs; 20% VPs; 40% Executive Directors, Senior Directors, and Directors
Automating Safety: The Surging Tide Reshaping Pharmacovigilance Operations
Regarding AE monitoring and intake practices, a majority (43%) reported a current automation level of 40%. Nonetheless, respondents expressed strong confidence in witnessing a significant automation boost over the next year, with 42% aiming for an automation level of 80% and above. This trend signifies growing acknowledgment of the benefits of automation, such as heightened efficiency, precision, and compliance, in managing and monitoring adverse events related to pharmaceutical products.
In aggregate reporting, more than half of the respondents currently operate at a mere 40% automation level. Notably, no organization has achieved an 80% or 100% automation rate. Over the next 12 months, a considerable 47% aim to elevate their level of automation to 60%.
As for signal and risk management, the existing automation levels within organizations are diverse: 44% reported a 40% automation rate, while only 4% noted an 80% automation rate. In the next 12 months, a large number (78%) expect to be in the 60% automation category.
AI/ML: Unlocking Secrets in Pharmacovigilance for a Safer Tomorrow
The potential of AI/ML algorithms lies in uncovering concealed patterns within adverse event data, enabling timely identification of safety signals, and seamlessly automating routine tasks. Although some organizations have made headway in embracing AI/ML, substantial room for growth and innovation remains within the PV sector. As industry progresses, entities which strategically leverage advanced technologies will fortify their safety monitoring capabilities, contributing to enhanced patient outcomes and drug safety while fostering more consistent and efficient workflows.
Yet, the pivotal query persists: Can technology genuinely steer superior outcomes in PV? A majority of respondents hold faith in technology’s transformative potential, with 45% foreseeing midlevel efficiency gains. More than 42% of these professionals believe technology adoption will significantly enhance decision-making processes. This collective optimism underscores the industry’s acknowledgment of technology as a catalyst for positive transformation, poised to elevate efficiency, scalability, decision-making, and regulatory compliance across the spectrum.
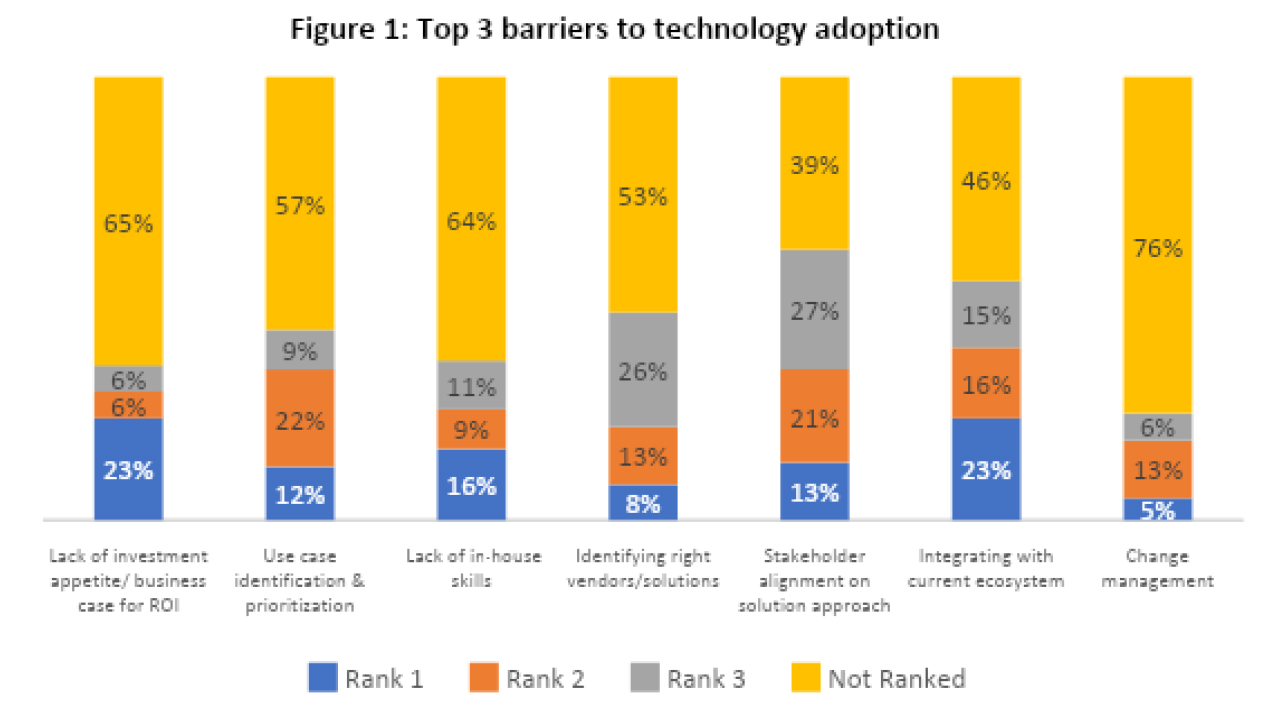
So, what impedes technology adoption? According to the bar chart (Figure 1), the primary barriers encompass a lack of appetite for investment/business case for ROI, challenges in integrating with the existing PV operational ecosystem, and a deficit of in-house skill sets.
Strategic Outsourcing: The Silent Force Steering Pharmacovigilance Evolution
Moreover, organizations are calling for enhancements in flexibility, alignment with long-term goals, and innovation from their outsourcing partners. Nearly half of the organizations currently delegate 40% of their AE monitoring and intake processes, highlighting a significant reliance on external expertise for this critical PV function. Similarly, aggregate reporting leans heavily towards outsourcing, with a remarkable 1 in 2 organizations presently outsourcing the lion’s share of these operations. This trend suggests that many organizations prefer to entrust the intricate task of aggregate reporting to external collaborators, involving the compilation and analysis of safety data over prolonged periods.
Despite the prevalence of outsourcing, only a small fraction of organizations choose complete outsourcing, with less than 5% outsourcing 100% of AE monitoring and intake activities. It underscores the importance these organizations place on maintaining some level of internal control and oversight in these pivotal areas. Looking ahead, the data point to a potential surge in higher levels of outsourcing in the coming year, especially in functions like case processing and aggregate reporting. This inclination likely stems from the desire to streamline operations and access specialized resources while retaining a degree of in-house management.
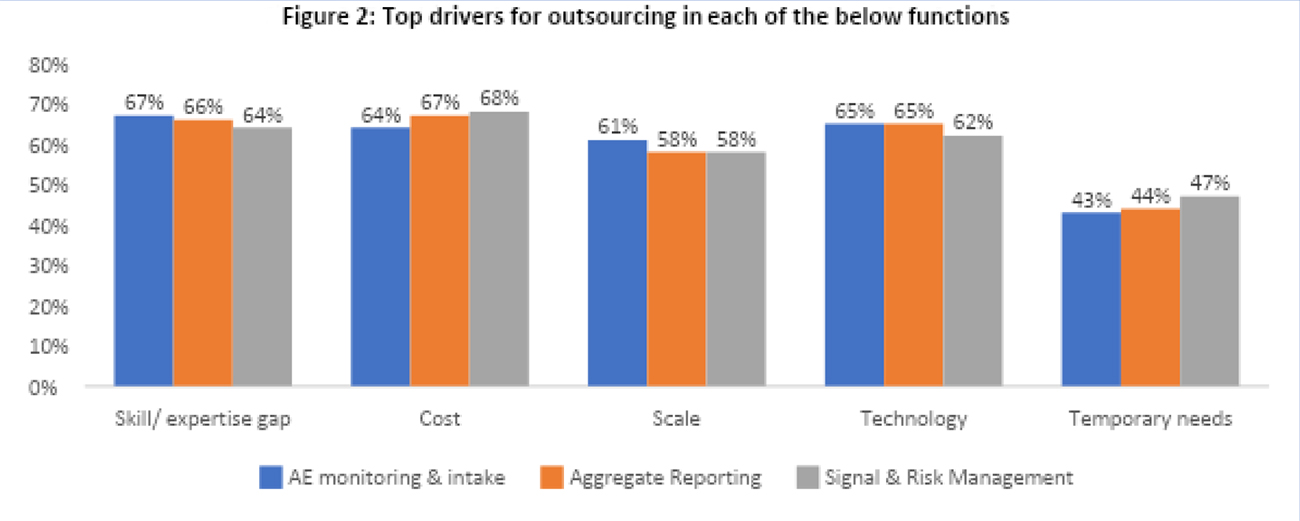
Primary drivers for outsourcing in PV functions differ but converge on common themes (Figure 2). “Skill/Expertise Gap” emerges as the primary driver in AE monitoring and intake, while “Cost” takes precedence in aggregate reporting and signal and risk management. Across all functions, organizations emphasized the importance of cost-efficiency, expertise, and technological advancements when making outsourcing decisions. At the same time, considerations of scalability and temporary resourcing needs also played a significant role in shaping these decisions.
Conclusion: Charting the Path Ahead
- Commit to technological advancements and automation to remain competitive and ensure operational efficiency. Explore the integration of real-time alert systems and AI/ML algorithms to enhance the precision and swiftness of safety signal detection and AE monitoring.
- Forge vendor relationships aligned with long-term strategic objectives and seek innovative solutions to enhance PV workflows.
- Assess outsourcing approaches to leverage specialized expertise while retaining a degree of internal oversight and control.

