Around the Globe
Summary and Impact of Pharmaceutical & Medical Device Act Amendments in Japan
Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K
his summary of the revision of Japan’s Pharmaceutical Affairs Act (PMD-Act) issued in December 2019 focuses on two of its three pillars and their impact on companies in Japan. The contents of this revision are broad, they include three pillars and will be implemented by the Government in a stepwise approach over three years:
- Improvement of systems from development to post-marketing in order to provide pharmaceutical and medical device products safely, quickly, and efficiently.
- Review of the community roles of pharmacists and pharmacies to improve patient familiarity and peace of mind with using pharmaceutical products.
- Establishment of regulatory compliance systems to further trust in the healthcare community of Japan.
This article will explore the implementation status and anticipated future impacts of pillars 1 and 3.
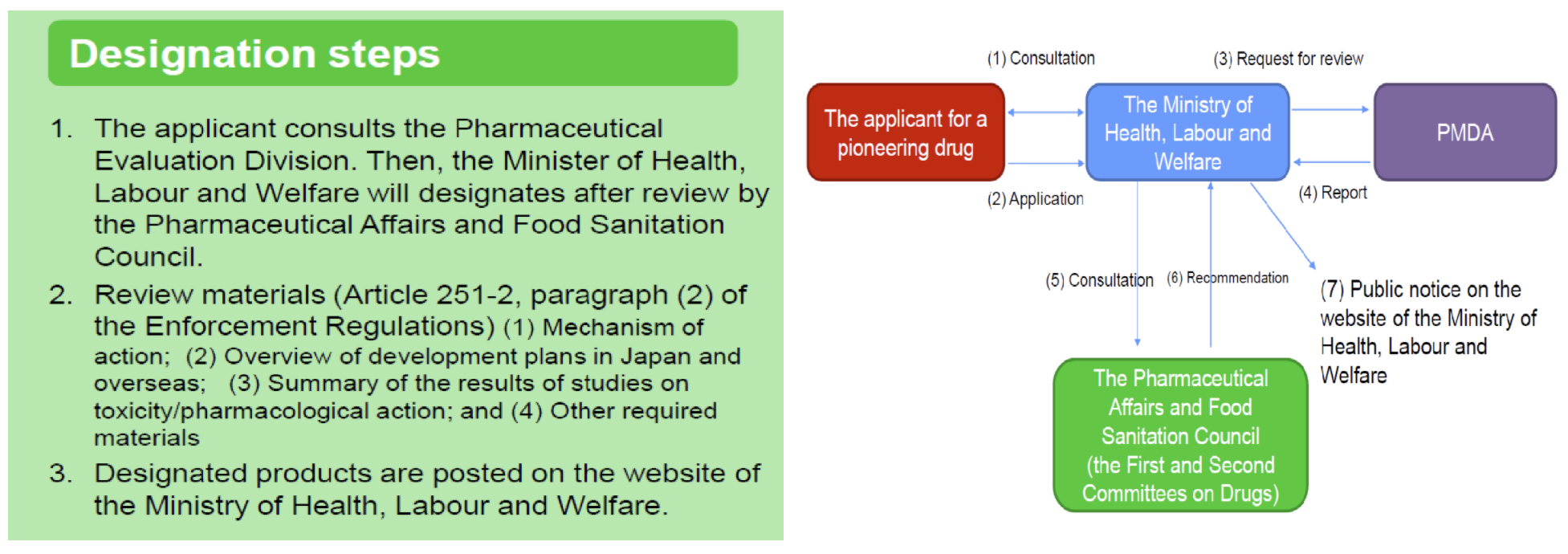
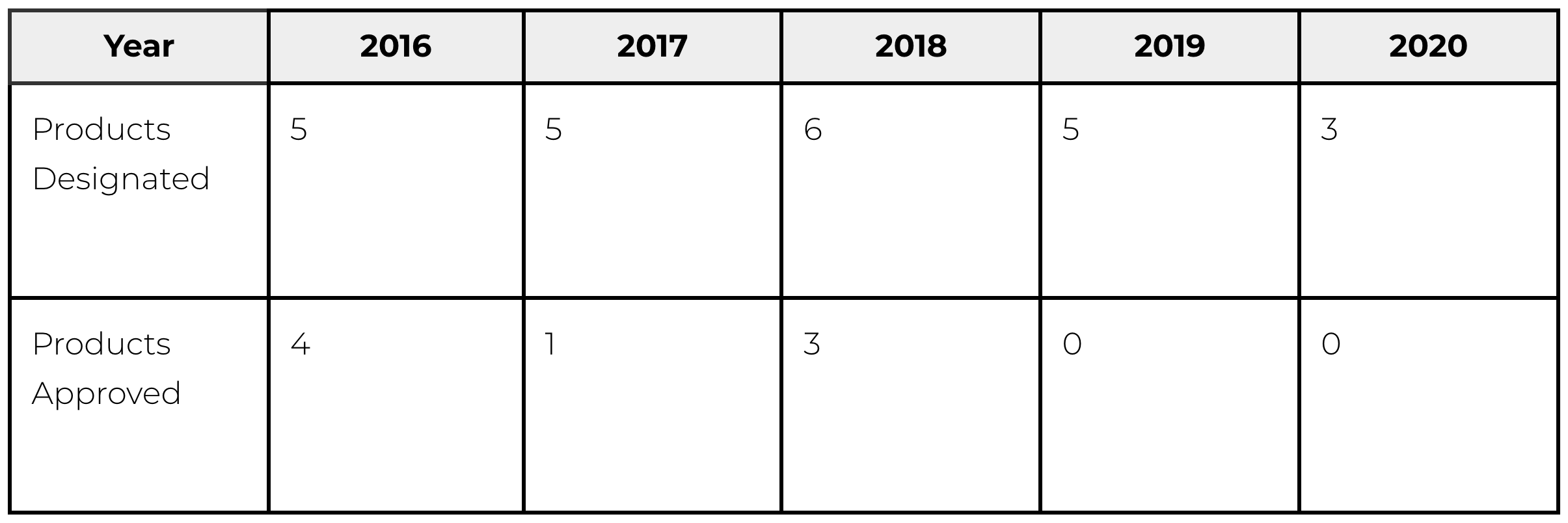
Improvement of Systems: Sakigake Designation
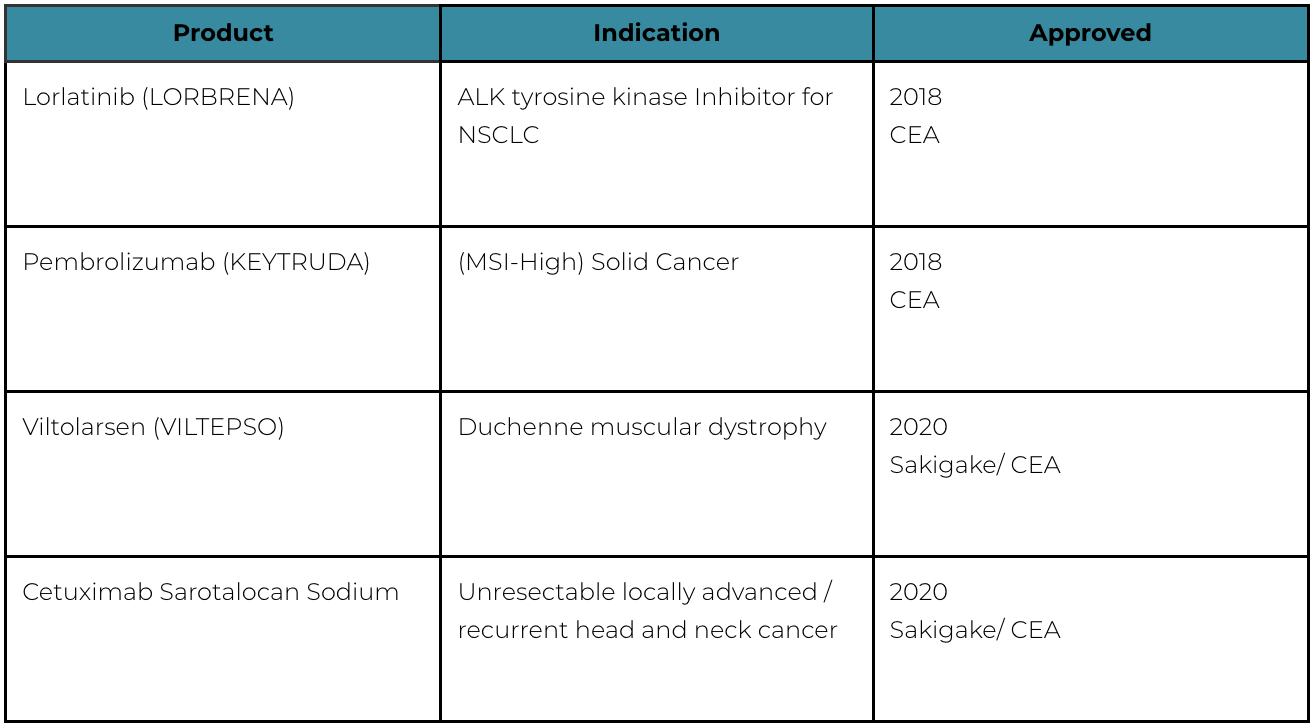
Improvement of Systems: Conditional Early Approval
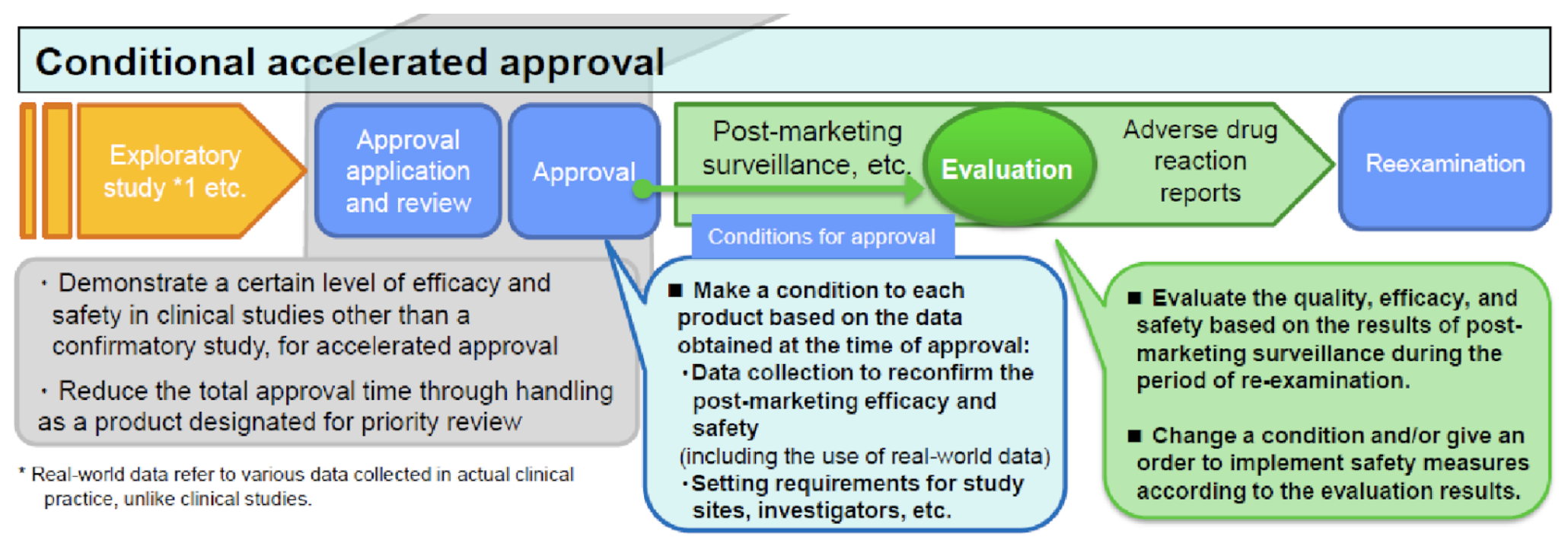
To alleviate safety concerns in the absence of a confirmatory study, this CEA system features an interim evaluation that allows for early identification and mitigation of safety concerns. As illustrated below, the sponsor commits to submitting interim post-approval safety results according to a specific timeline. Based on these interim results, the sponsor may be directed to change the indication, dose or administration, or precautions in the package insert, for the approved product. This system allows innovative products to quickly reach patients with unmet medical needs and also allows for continued safety evaluation while patients use them. This CEA pilot program was made permanent effective September 1, 2020.
Improvement of Systems: System for Drugs for Specific Use
Furthering Trust: Clinical Trial Notification and Safety Reporting in Clinical Development
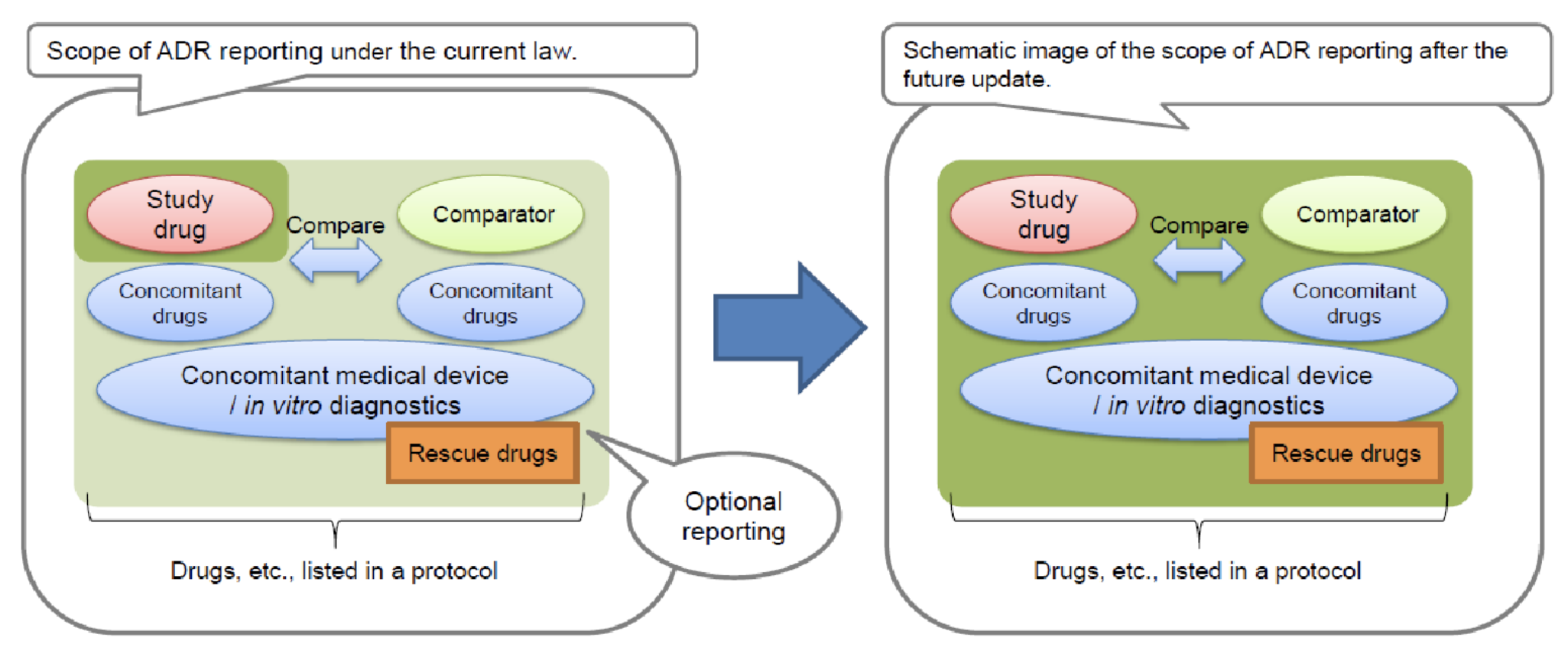
**All Drugs means not only the main compound being studied but also concomitant drugs, rescue drugs, or other approved drugs mentioned in the study protocol.
Looking Forward
We must now enter a period of collecting, analyzing, and understanding the results of these changes to identify their impact on industry, health authorities, regulatory bodies, and patients in Japan, and to determine our best next steps for the future implementation stages.
All figures based on an October 22, 2020, briefing by the Federation of the Pharmaceutical Manufacturers’ Associations of Japan (FPMAJ).

